Unilateral hyperacusis as indicated via interaural asymmetry in ULLs
Unilateral hyperacusis as indicated via interaural asymmetry in ULLs
There is little information in the literature about between-ear differences in uncomfortable loudness levels (ULLs) for patients with hyperacusis (Aazh et al. 2018; Aazh et al. 2014). Hyperacusis is usually considered as a binaural condition. In fact, some authors suggested that hyperacusis is exclusively bilateral (Baguley & Hoare 2018). To the contrary, the research conducted by Dr. Aazh’s tinnitus team highlighted the prevalence and characteristics of patients with large interaural asymmetry in ULLs which is an indication of unilateral hyperacusis.
A large between-ear difference in ULLs might indicate some specific abnormality in monaural pathways. Further studies of people with large between-ear differences in ULL could give some insight into whether the intolerance to sound is mainly due to increased loudness perception in the ear with lower ULLs (which could be studied by comparing the loudness of sounds presented alternately to the two ears), to a dislike of specific sounds when presented to that ear, or to a dislike of a class of sounds with certain spectral characteristics.
If a global psychological or neurological component is predominant in producing hyperacusis, then it seems unlikely that it would affect one ear more than the other.
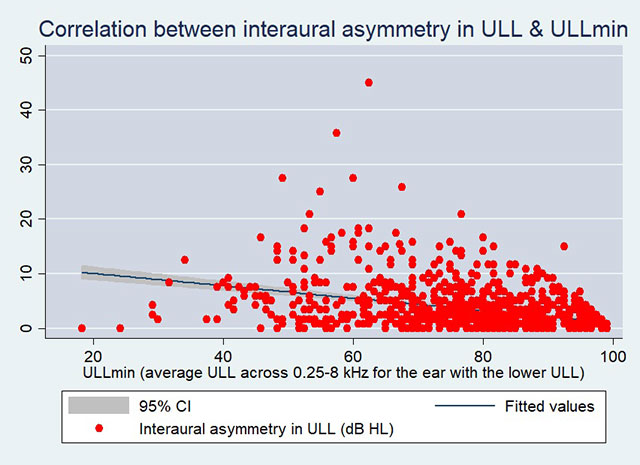
Dr. Aazh’s tinnitus team conducted a pioneering study exploring the differences in average ULLs between the two ears (interaural asymmetry in ULL ) in over 800 patients with tinnitus and/or hyperacusis. This study was published in International Journal of Audiology. Approximately, 8% of the patients had a between-ear difference of 10 dB or more. About 80% of patients with interaural asymmetry in ULL ≥10 dB were also diagnosed as having hyperacusis based on the ULLmin criteria (i.e., average ULL across 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4 and 8 kHz for the ear with the lower average ULL, ULLmin, equal to or below 77 dB HL) (Aazh & Moore 2017). This was significantly higher than the 33% of patients with interaural asymmetry in ULL <10 dB HL who were diagnosed as having hyperacusis based on the ULLmin criteria (p<0.001). There was a statistically significant negative correlation between interaural asymmetry in ULL and ULLmin as shown in the graph below (r=-0.35, p<0.001).
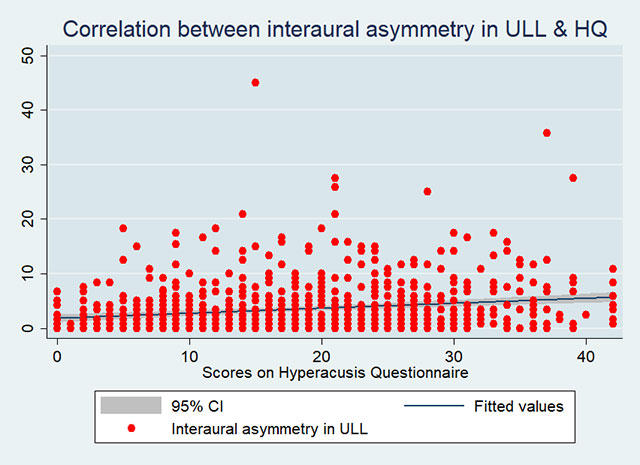
For patients with a between-ear difference in ULL of 10 dB or more, the mean score on the HQ was 22 (SD = 8). This was significantly higher (worse) than the mean HQ score of 17.6 (SD = 9.5) for the remainder of the patients (p = 0.007). There was a statistically significant correlation between interaural asymmetry in ULL and scores on HQ as shown in the graph below (r=0.2, p<0.001).
Clinical implications
A large interaural asymmetry in ULLs is associated with a lower (worse) ULLmin indicating more severe hyperacusis and a higher HQ score indicating more server impact of hyperacusis on patient’s life.
References
Aazh, H., Knipper, M., Danesh, A. A., et al. (2018). Insights from the third international conference on hyperacusis: causes, evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment. Noise Health, 20, 162-170.
Aazh, H., McFerran, D., Salvi, R., et al. (2014). Insights from the First International Conference on Hyperacusis: causes, evaluation, diagnosis and treatment. Noise Health, 16, 123-6.
Aazh, H., & Moore, B. C. J. (2017). Factors related to Uncomfortable Loudness Levels for patients seen in a tinnitus and hyperacusis clinic. International Journal of Audiology 56, 793-800.
Baguley, D. M., & Hoare, D. J. (2018). Unanswered questions in hyperacusis. HNO, 66, 358-363.
Read MoreCookie settings
REJECTACCEPT
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __stripe_mid | 1 year | Stripe sets this cookie cookie to process payments. |
| __stripe_sid | 30 minutes | Stripe sets this cookie cookie to process payments. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | Set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin, this cookie is used to record the user consent for the cookies in the "Advertisement" category . |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _ga | 2 years | The _ga cookie, installed by Google Analytics, calculates visitor, session and campaign data and also keeps track of site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookie stores information anonymously and assigns a randomly generated number to recognize unique visitors. |
| _gat_gtag_UA_131443801_1 | 1 minute | Set by Google to distinguish users. |
| _gid | 1 day | Installed by Google Analytics, _gid cookie stores information on how visitors use a website, while also creating an analytics report of the website's performance. Some of the data that are collected include the number of visitors, their source, and the pages they visit anonymously. |
| CONSENT | 2 years | YouTube sets this cookie via embedded youtube-videos and registers anonymous statistical data. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE | 5 months 27 days | A cookie set by YouTube to measure bandwidth that determines whether the user gets the new or old player interface. |
| YSC | session | YSC cookie is set by Youtube and is used to track the views of embedded videos on Youtube pages. |
| yt-remote-connected-devices | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the video preferences of the user using embedded YouTube video. |
| yt-remote-device-id | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the video preferences of the user using embedded YouTube video. |
| yt.innertube::nextId | never | This cookie, set by YouTube, registers a unique ID to store data on what videos from YouTube the user has seen. |
| yt.innertube::requests | never | This cookie, set by YouTube, registers a unique ID to store data on what videos from YouTube the user has seen. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| m | 2 years | No description available. |



